
Welcome to Q-BioLiP
Q-BioLiP is an updated version of the original BioLiP database for protein-ligand interactions. One of the major improvements over BioLiP are the protein-ligand interactions are based on quaternary structure rather than single-chain monomer structure. DNA/RNA chains are also paired rather than separated. To predict the ligand-binding site for new structures, Q-SITE can be used. Read more about the Q-BioLiP...
For each structure from PDB (in mmCIF format), the following annotation data are provided in Q-BioLiP:
Statistics (Version 2025-04-25)
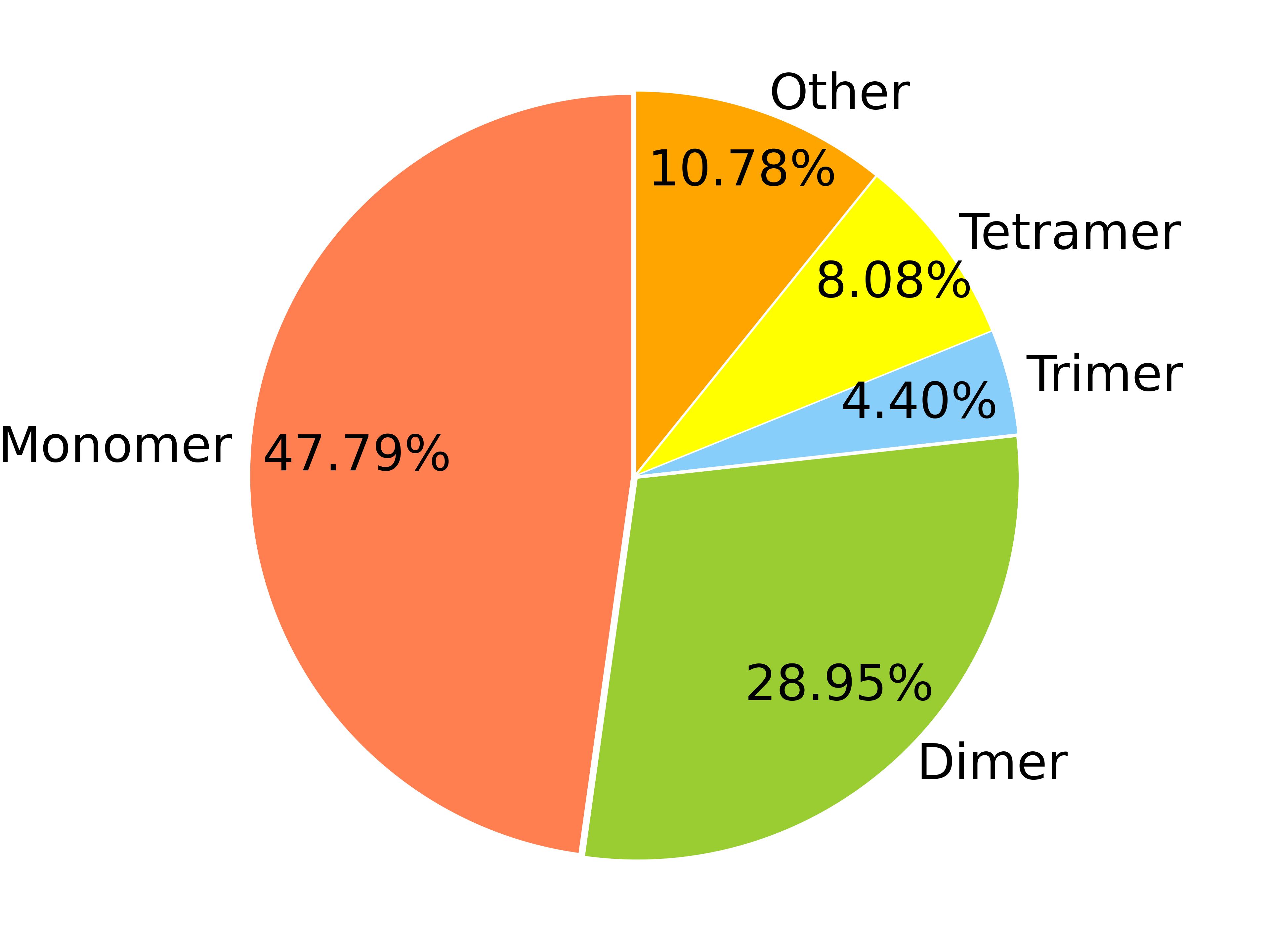
- monomers: 106,153
- dimers: 64,303
- trimers: 9,762
- tetramers: 17,942
- others: 23,947
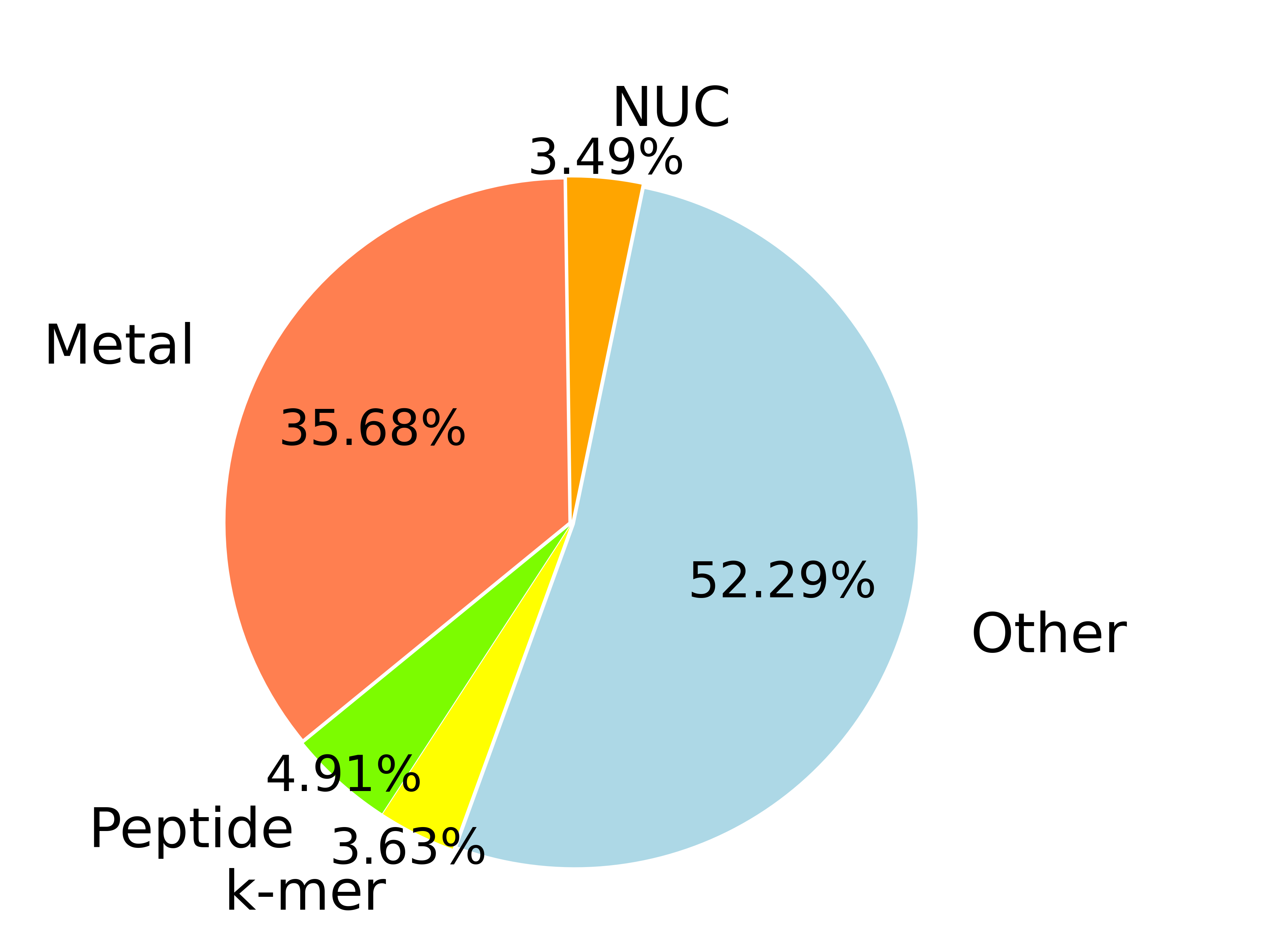
- peptides: 52,307
- nucleic acids: 37,185
- metal ions: 380,429
- k-mers: 38,705
- other ligands: 557,508
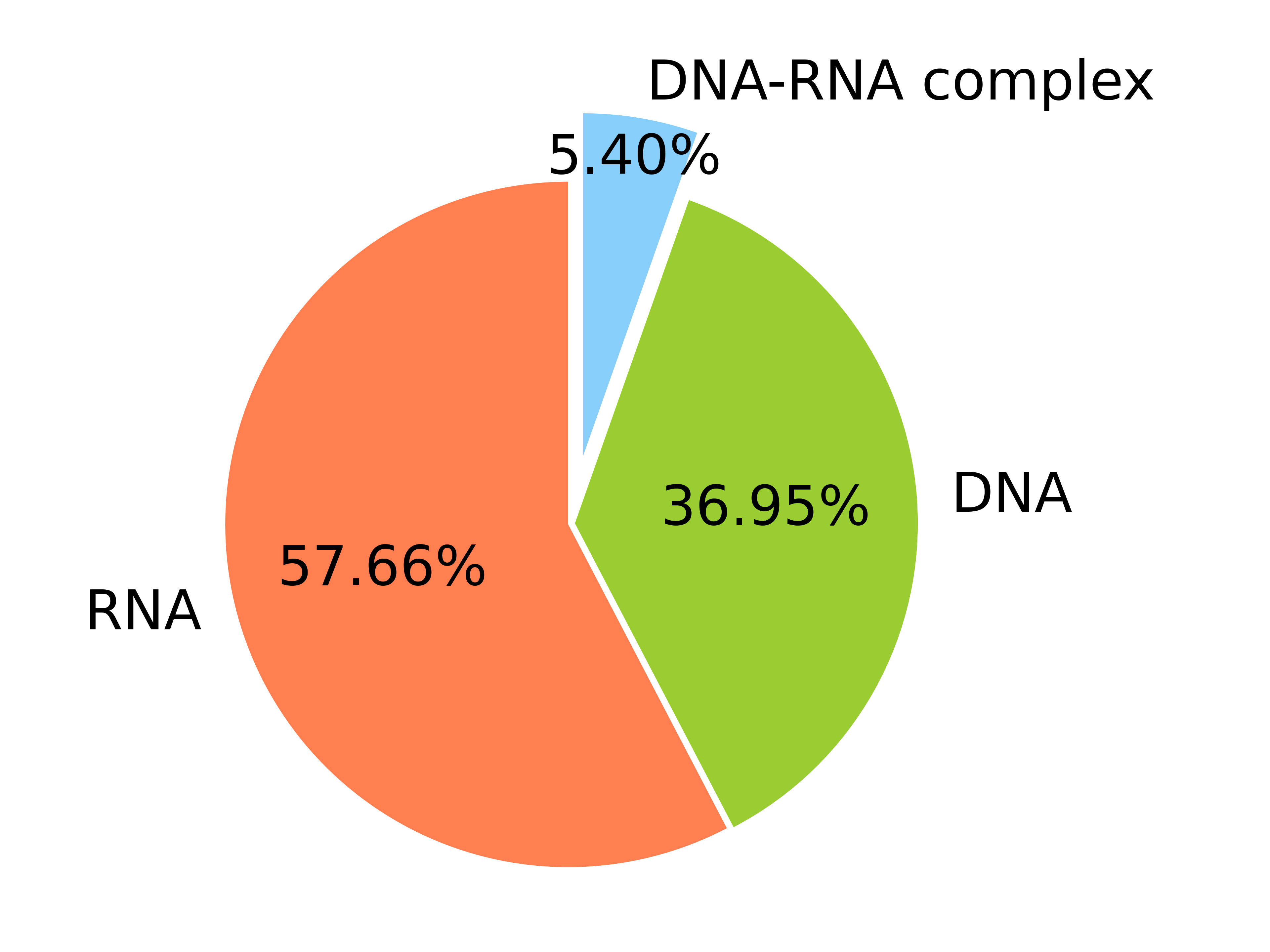
- DNAs: 13,738
- RNAs: 21,440
- DNA-RNAs: 2,007
Browse Q-BioLiP
Biologically relevant interactions
The ligands are biologically relevant and interact tightly with the protein structures. This is the core data of Q-BioLiP, containing 1,066,134 entries.
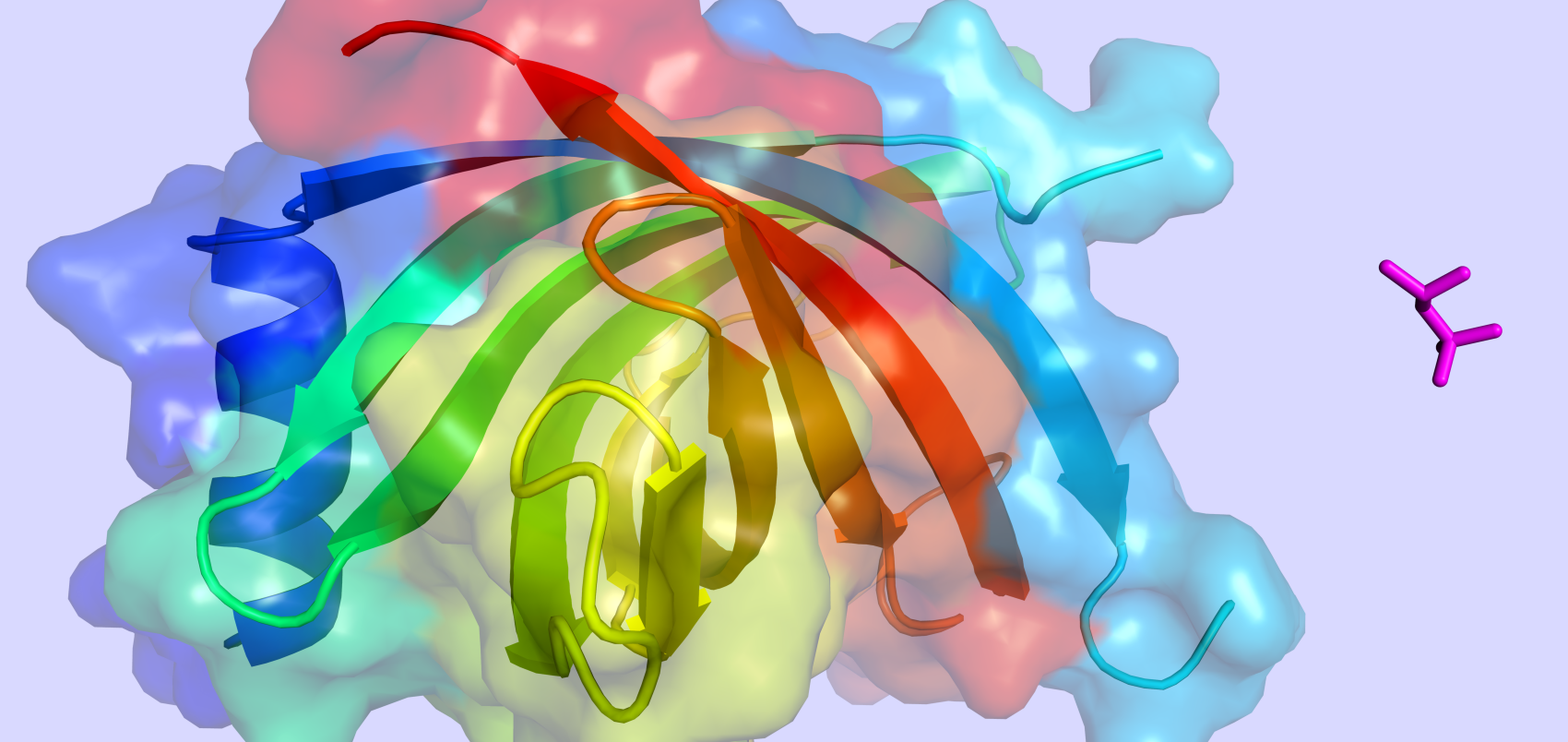
Biologically irrelevant interactions
The structures contain both proteins and ligands, but without biologically relevant interactions. It contains 1,957,118 entries.
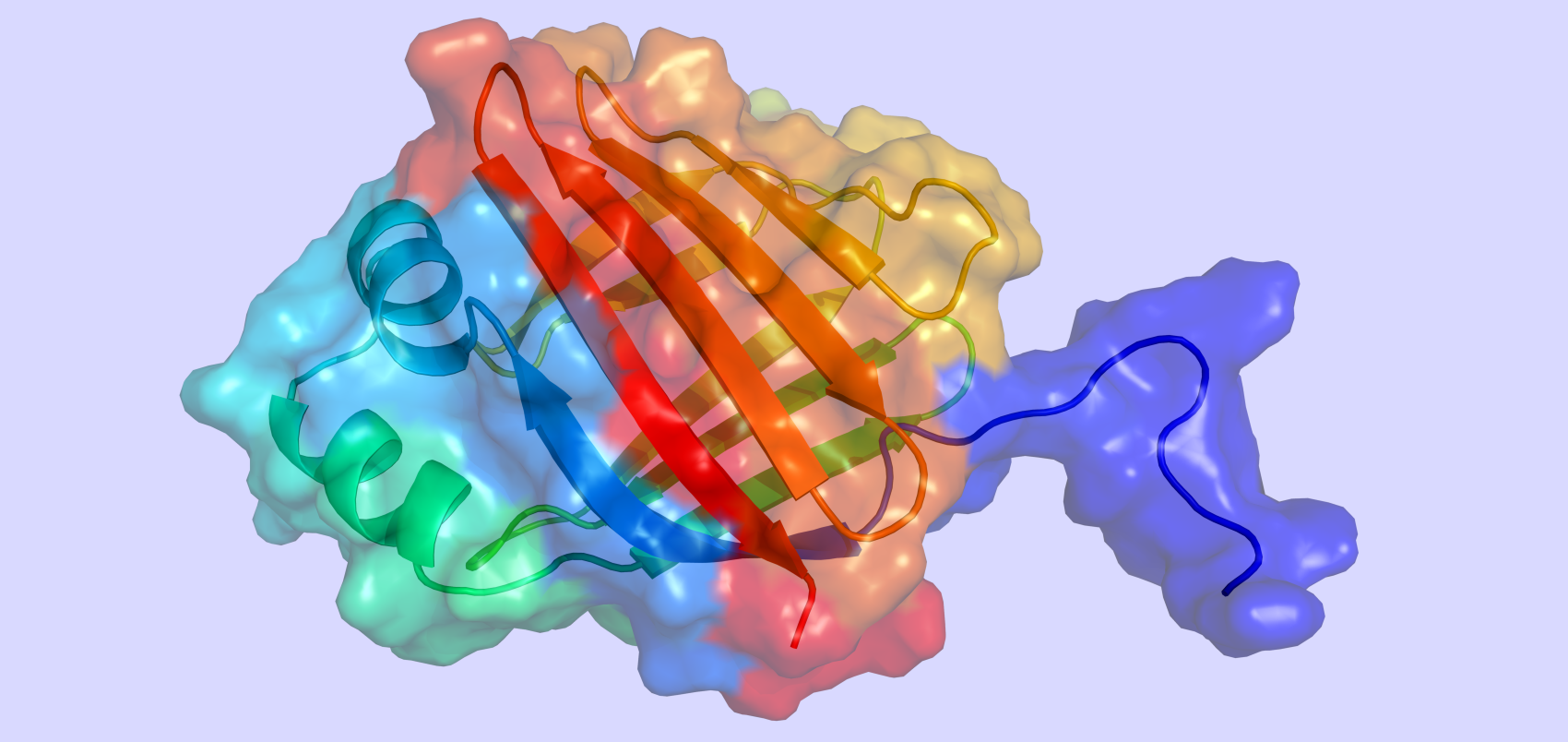
Structures with proteins/ligands only
The structures contain proteins/ligands only. It contains 74,882 entries.
Reference